Causes and treatment of periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tooth support. Such dental disease occurs frequently. It is characterized by gradual development, so the patient notices already in the later stages, when the disease seriously damaged soft tissues. Therefore, it is recommended that everyone visit a dentist every six months to prevent the occurrence of such problems.
Causes of occurrence
Common causes of periodontitis are:
- Poor oral care;
- Insufficient blood supply to the gums (observed in smokers);
- Vitamin deficiency (seasonal problem).
Less commonly, the disease appears when the gums are damaged. For example, if the patient damaged the surface with sharp nuts or other food.
Periodontitis treatment is a procedure that needs to be started promptly. Disregarding or putting aside professional assistance, the risk of losing teeth increase.
Symptomatology
At the first stage, the disease proceeds unnoticed for a person. The main symptom is bleeding gums. In this case, there is no pain. Blood appears during mechanical manipulations, for example, during brushing. The patient may think that he put too much pressure on the brush, due to which micro damages were formed. When bleeding regularly, rather than occasionally, you need to consult a doctor.
The second stage is characterized by symptoms:
- An unpleasant odor that cannot be eliminated by regular oral care.
- Gum prolapsus, friability and excessive softness.
- Teeth seem visually longer.
The stage is accompanied by bleeding not only during brushing. Even when eating, metallic taste may occur.
In the third stage, pain appears. The legs of the teeth are exposed, because gums sink too low. The roots and nerve endings are no longer protected by gum, therefore the oral cavity reacts strongly to minimal changes in temperature or acid (for example, when eating lemon). If you do not start treatment of periodontitis, the body will fight independently – will increase the temperature, dizziness appear.
Periodontitis treatment
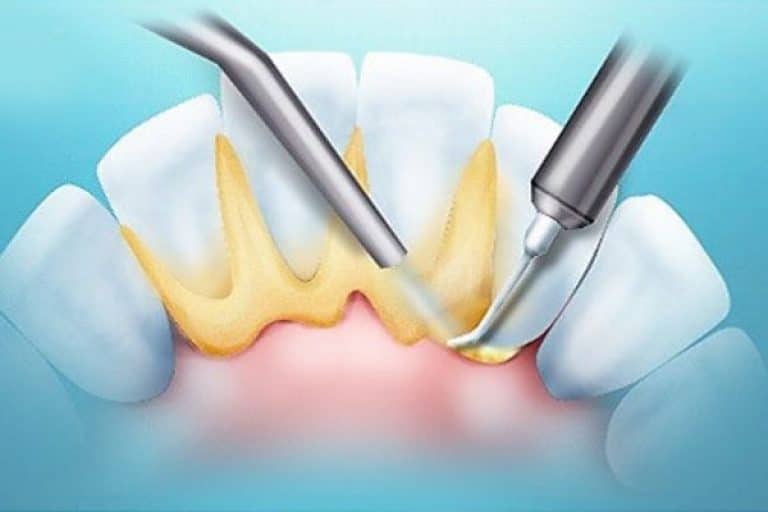
First, the dentist removes plaque and deposits. Because of them, the gums during the treatment process will not be able to restore their previous normal position. Next, local antiseptics are used. If you do not disinfect the affected areas, inflammation and abscess can move on to other soft tissues.
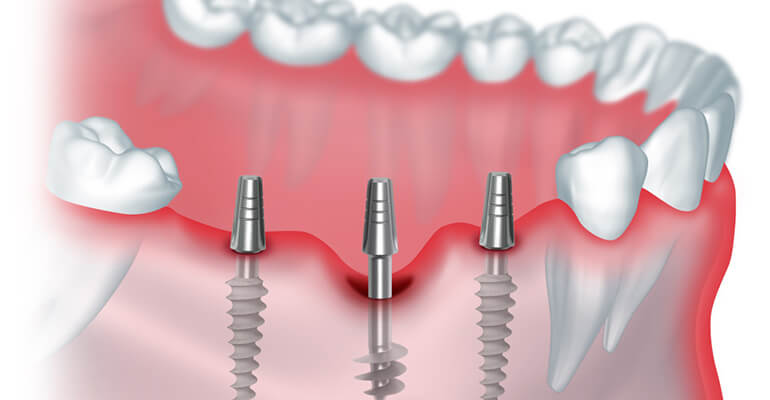
When the disease continues, only the surgical treatment of periodontitis will help. The gum is incised and the affected area is washed out. Sometimes implantation of artificial tissue is required in place of the excised area.
For prevention, you should regularly clean the oral cavity not only with a toothbrush, but also with floss and special rinses.